INTENDED USE
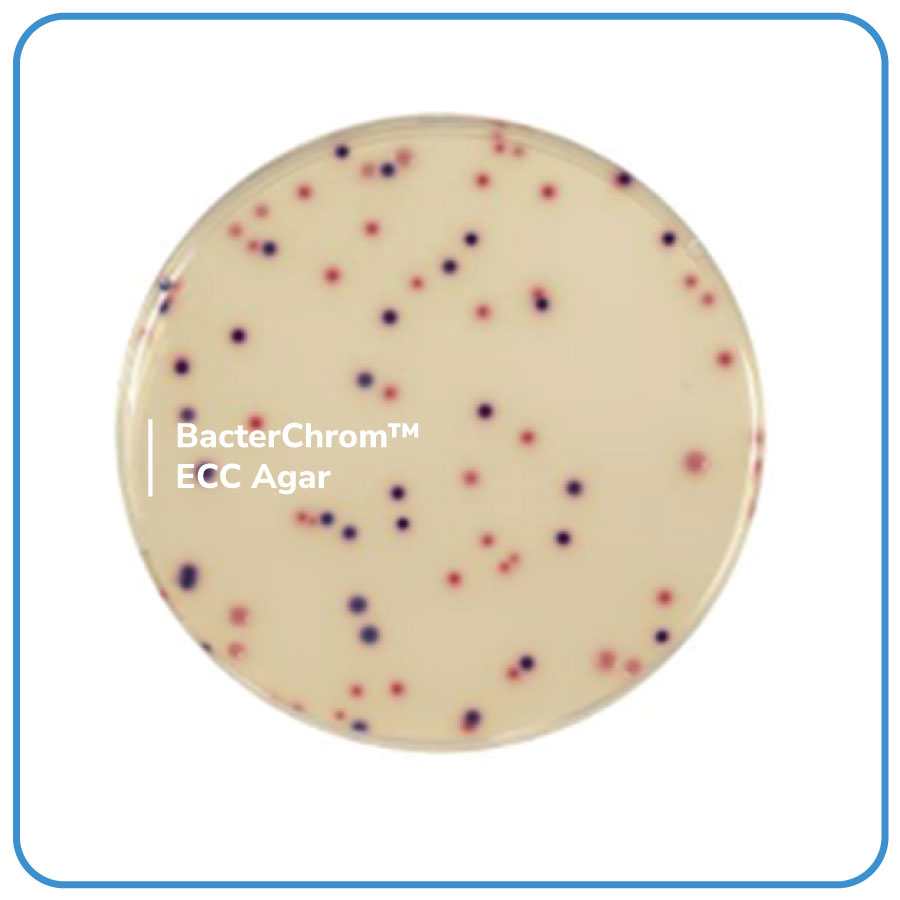
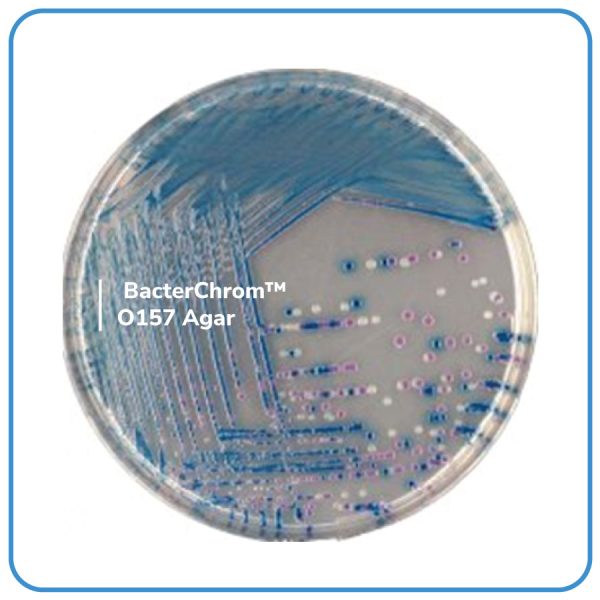
- BacterChrom™ ECC Agar s a selective agar for the simultaneous and specific enumeration without confirmation of Escherichia coli and of other coliform bacteria in human and animal food.
- The packaging with semi-permeable Cellophane film helps balance the humidity of the environment during storage.
PRINCIPLES
- The classification of coliforms is traditionally founded on their capacity to ferment lactose with a corresponding production of acid. The fermentation of lactose results from the successive cascade effect of two enzymes : first a permease responsible for the penetration of the sugar into the bacteria, and then a β-galactosidase which cuts the glucose to galactose, thereby actively entering into the fermentation process.
- In 1989, Leclerc & Mossel proposed that the presence of β – galactosidase with coliforms be used as the main criteria for classification. The use of a synthetic chromogenic substrate, insensitive to variations in the permeability of lactose, allows the use of this enzyme by a colorimetric reaction.
- 94 to 97% of Escherichia coli possess a β-D-glucuronidase activity and that the same activity is only rarely encountered with other species (enzyme activity has been detected in a small number of strains of Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Salmonella, Shigella and in Yersinia)

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt